Describe What Happens at Each Step in the Gram Stain
Make smear according to previous exercise. Iodine is added and acts as a mordant and causes the crystal violet to form large crystals within the cell wall leave on for 1 min 5.
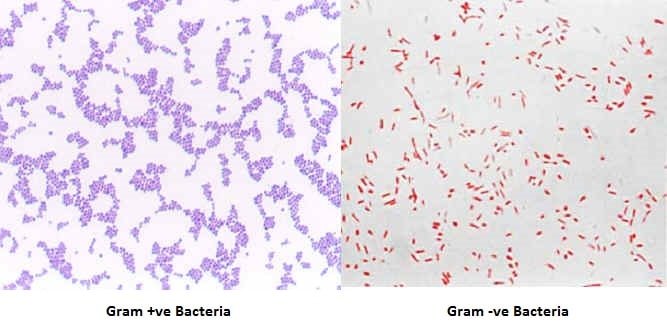
Gram Staining Principle Procedure Interpretation Examples And Animation
Solution for What is Gram stainingDescribe step by step the procedure.

. Decolorizing with ethanol 5. Subsequently a decolorizer often solvent of ethanol and acetone is used to remove the dye. How are the results of a Gram stain important in prescribing a treatment for a bacterial infection.
Next a Grams iodine solution iodine and potassium iodide is added to form a complex between the crystal violet and iodine. Gram- bacteria lose the crystal violet color after decolorizing with. Describe the Gram stain technique and the effect on Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria after each step.
Initially the sample is stained with crystal violet dye. Describe what happens to. Both gram-positive and gram-negative cells have peptidoglycan in their cell walls so initially all bacteria stain violet.
Enter cytoplasm and colors all cells that can be stained 2 Iodine complexes with crystal violet acting as a mordant to enhance affinity of cellular components for dye 3 Acetonealcohol removes crystal violet- iodine complex from gram negative cells. Why does alcohol easily decolorize gram-negative bacteria but not those that. Heat-fixing adheres the smear to the slide and hence makes it less amenable to being washed away during gram-staining procedure.
At the end of the gram staining procedure gram negative cells will be stained a reddish-pink color. The primary stain is the first dye applied in differential staining and generally stains all cells. Crystal violet is primary stain leave on for 1 min 3.
The first step in gram staining is the use of crystal violet dye for the slides initial staining. The next step also known as fixing the dye involves using iodine to form crystal violet- iodine complex to prevent easy removal of dye. 1 Crystal violet is the primary stain entering the cytoplasm and imparting a color to all cells that can be stained.
The Gram stain involves staining bacteria fixing the color with a mordant decolorizing the cells and applying a counterstain. 2 Iodine complexes with the crystal violet within the cell acting as a mordant to enhance the affinity of the cellular components for a dye. Procedure of Gram Staining Smear Preparation Fix material on a slide with methanol or heat.
Describe what happens in each step of a gram stain 1 Crystal violet is primary stain. Steps of Gram stain. Exposing gram negative cells to the decolorizer dissolves the lipids in the cell walls which allows the crystal violet-iodine complex to leach out of the cells.
The four basic steps of the Gram Stain are. Weve got the study and writing resources you need for. The smear is rinsed to remove excess primary stain and then flooded with a mordant.
The smear is flooded with the primary stain. This complex is a larger molecule than the original crystal violet stain and iodine and is insoluble in water. After decolorization the gram-positive cell remains purple in color whereas the gram-negative cell loses the purple color and is only revealed when the counterstain the positively charged dye safranin is added.
Counterstaining with crystal violet. CV dissociates in aqueous solutions into CV and Cl ions. This may be due to different versions or editions of the same book.
Gram staining using crystal violet allows the peptidoglycan layer of the Gram bacteria to pick up the dye and retain it even after decolorizing. The various steps involved in Grams staining are detailed below. Describe what happens at each step in the Gram stain.
First week only 499. Primary stain with safranin 3. What happens when you reverse safranin and crystal violet in gram stain procedure.
Please type the answer. 1 Application of the primary stain Crystal Violet CV to a heat-fixed smear of bacterial culture. The sample is adhered over the slide and is stained under the aseptic conditions.
You can subscribe if you decide the step-by-step solutions will be useful albeit the differences. The smear is rinsed to remove excess dye and then flooded with a solution called Grams iodine. Describe the Gram stain procedure.
Describe in detail what happens in each step. Gram-positive bacteria have only one lipid bilayer with a very thick layer of peptidoglycan. Describe the colors of both gram-positive and gram-negative cells after each of the four steps in the Gram staining method not including rinsing with water.
Include a name for each step and the correct names for all reagents used. Cells are stained with crystal violet dye. The smear is first flooded with the primary stain crystal violet usually.
Gram-negative bacteria contain two lipid bilayers with a thin layer of peptidoglycan separating the two membranes. You can check the table of contents and match the questions in each chapter As you can see the questions are free to view for the entire book. Be very specific about what is happening at each step and why it happens.
Describe what happens at each step in the gram stain. Featured Video The primary stain crystal violet binds to peptidoglycan coloring cells purple. Start your trial now.
Excess stain over the. The stained smear is rinsed again and then a decolorizing agent is added to removed the dye-mordant complex from the Gram negative cells. This allows the cells to subsequently be stained with safranin.
The process involves three steps. Chapter 231 Problem 3Q is solved. Step 1 of 5 The gram-staining is a procedure that differentiates bacteria by their cell wall.
These two ions then penetrate through the cell wall and cell membrane of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative cells. Be sure to mention what color are the cells AND WHY. Describe the appearance of a Gram positive and a Gram negative cell at each step of the procedure.
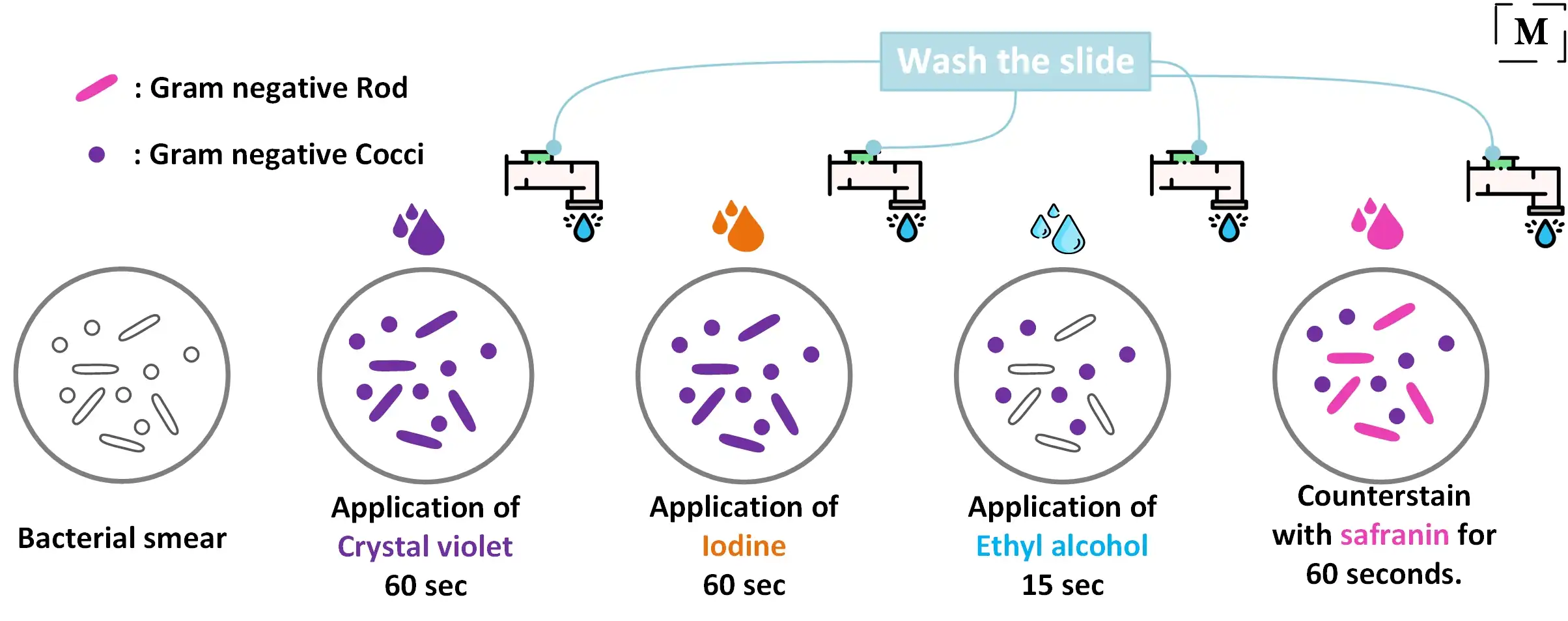
Gram Staining Better Understanding Of The Procedure And Easy Interpretation Of The Results
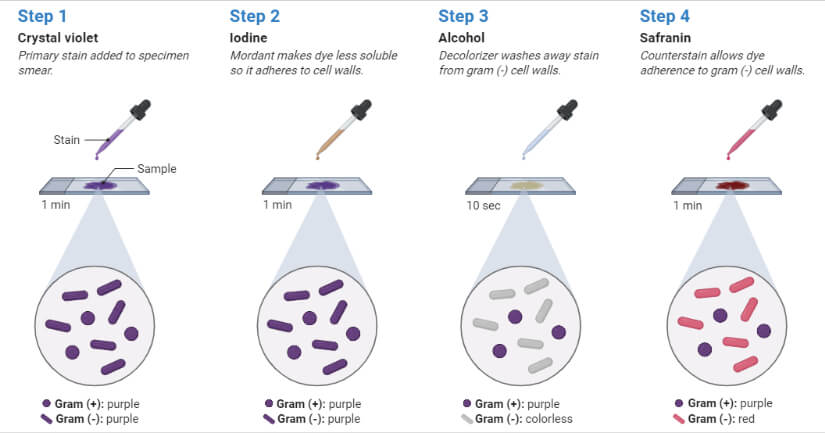
Gram Staining Principle Reagents Procedure Steps Results
Gram Staining Principle Procedure Results Microbe Online
What Purpose Does Gram Staining Serve Quora
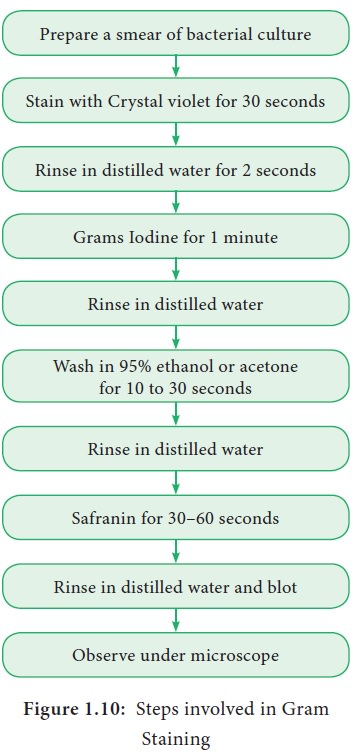
Gram Staining Procedure Bacteria
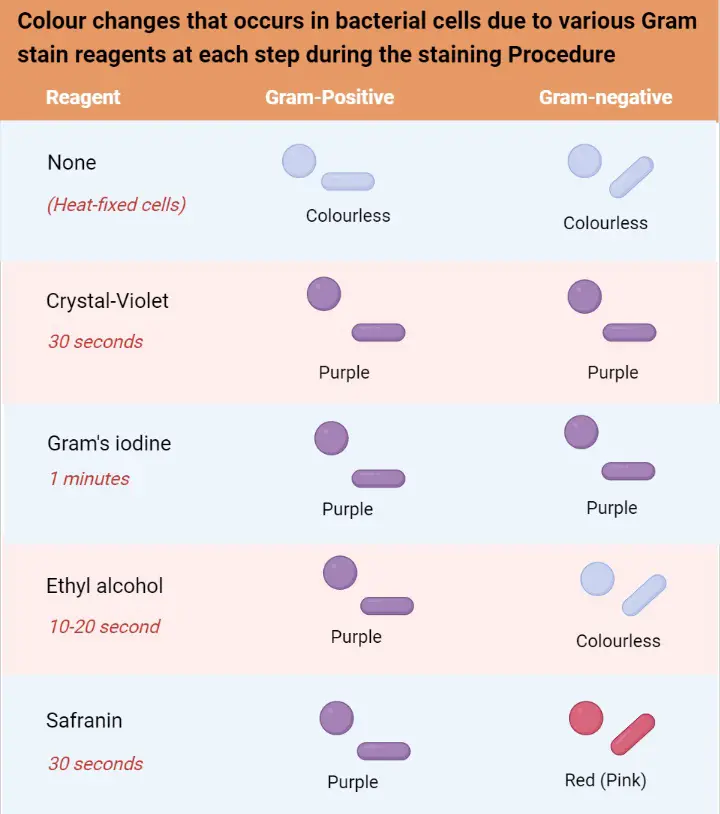
Gram Staining Procedure Principle And Results

Gram Staining Procedure Microbiology Medical Laboratory Technician Medical Laboratory Scientist

Gram Staining Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
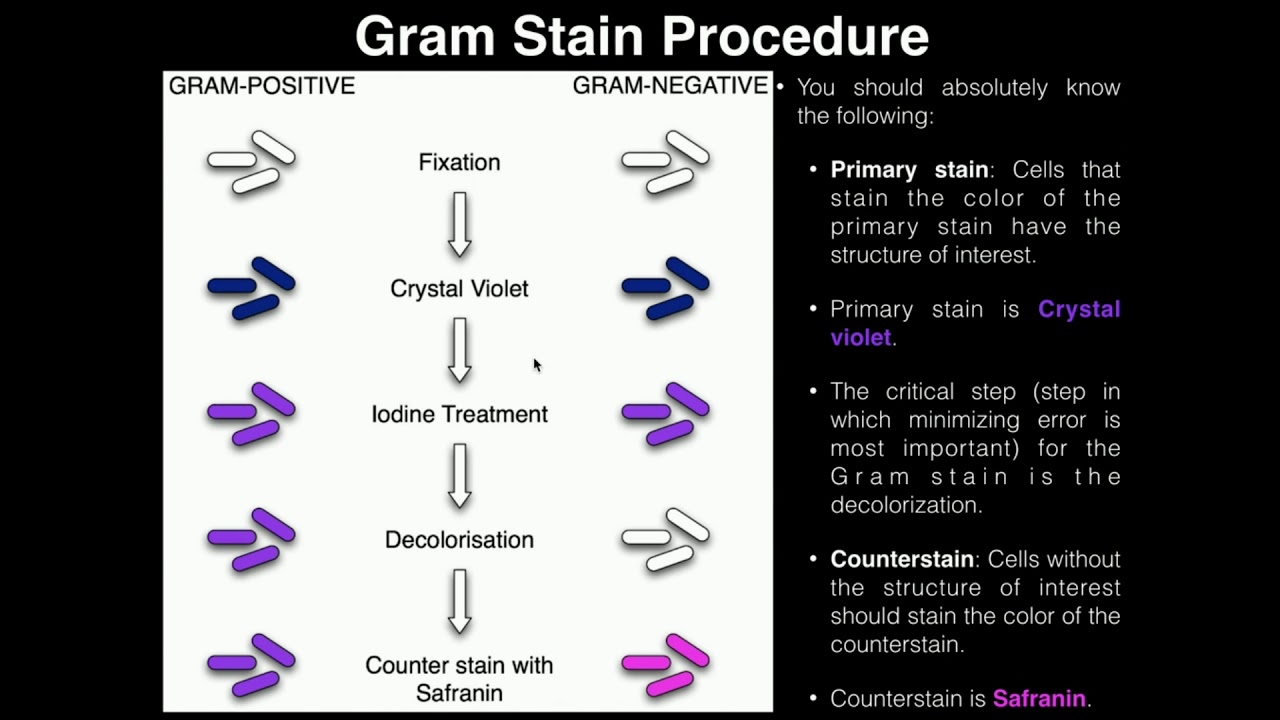
Lab Exercise 3 Heat Fixing And Gram Staining Youtube
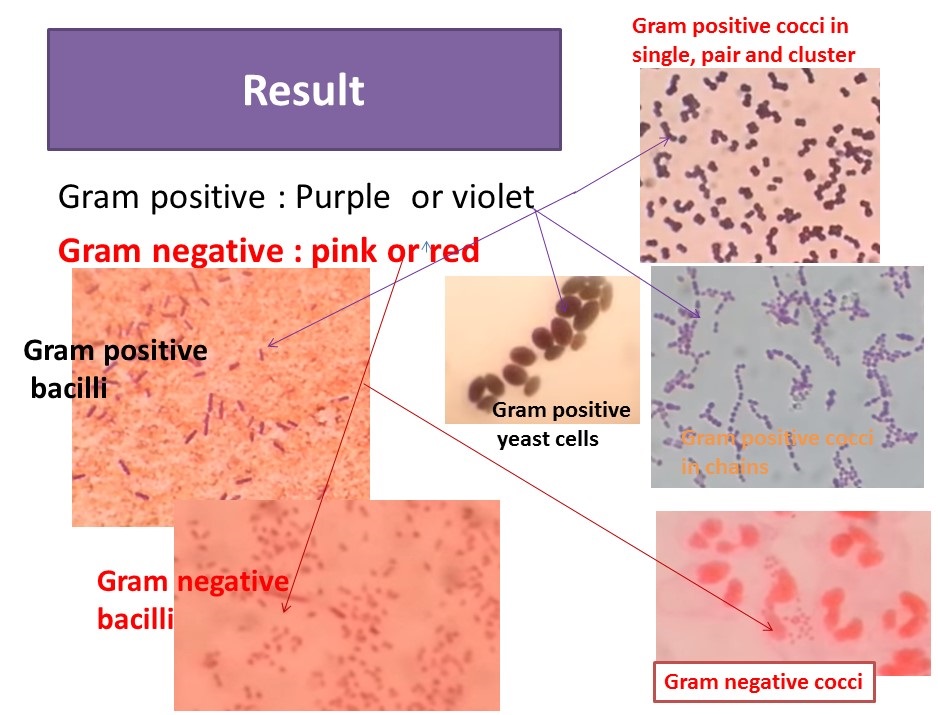
Gram Stain Introduction Principle Procedure Result And Interpretation
What Are The Mechanisms Of Gram Staining And How Do They Work Quora

Reagents Used In The Gram Stain Labster Theory
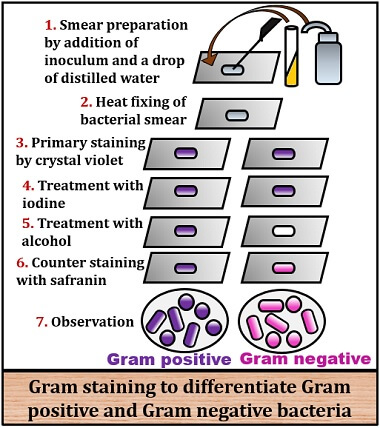
What Is Gram Staining Definition Video Principle Process Significance Biology Reader
/gram-positive-staphylococcus-aureus-bacteria-541802136-57979cca5f9b58461f26eccc.jpg)
Gram Stain Procedure In Microbiology



Comments
Post a Comment